Abstract
Overview Integrative analysis of genome-wide association studies (GWASs) and gene expression studies in the form of a transcriptome-wide association study (TWAS) has the potential to better elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying disease etiology. METRO can leverage gene expression data collected from multiple genetic ancestries to enhance TWASs.
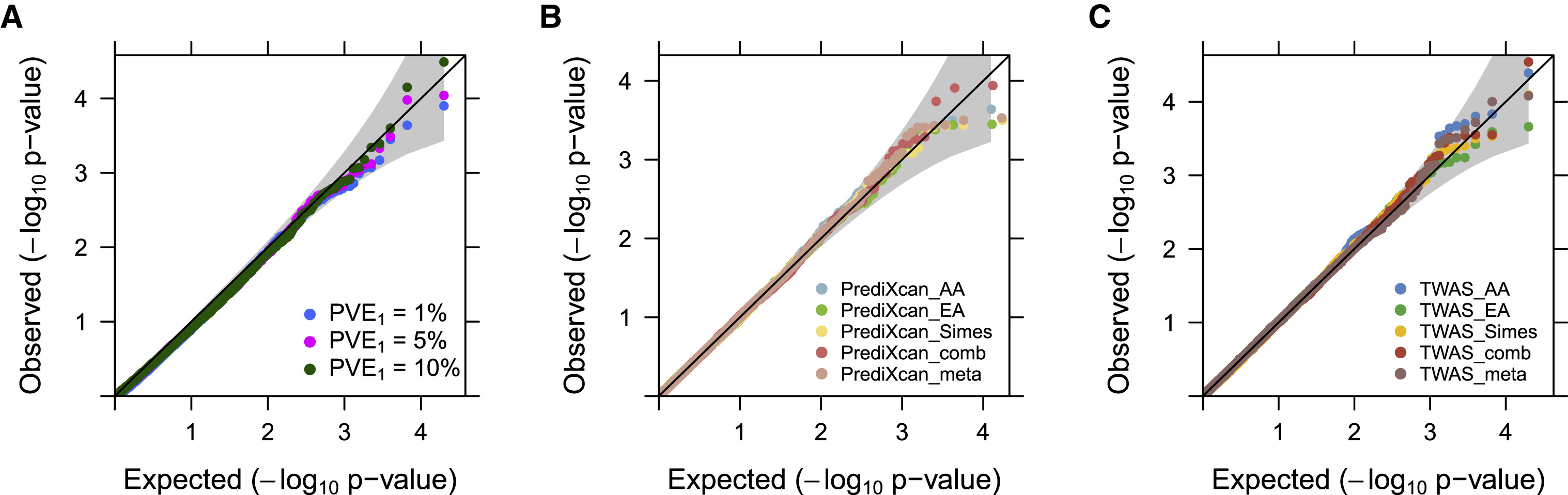
Materials and Methods METRO incorporates expression prediction models constructed in different genetic ancestries through a likelihood-based inference framework, producing calibrated p values with substantially improved TWAS power.
Results We illustrate the benefits of METRO in both simulations and applications to seven complex traits and diseases obtained from four GWASs. These GWASs include two of primarily European ancestry (n = 188,577 and 339,226) and two of primarily African ancestry (n = 42,752 and 23,827). The benefits of METRO are most prominent in applications to GWASs of African ancestry where the sample size is much smaller than GWASs of European ancestry and where a more powerful TWAS method is crucial.
Conclusion By leveraging expression data from multiple genetic ancestries and performing a TWAS in a joint likelihood framework, METRO can improve the power of the TWAS.
Paper:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.03.003
Pakcage of METRO
METRO