Abstract
Introduction Target organ damage (TOD) manifests as vascular injuries in the body organ systems associated with long-standing hypertension. DNA methylation in peripheral blood leukocytes can capture inflammatory processes and gene expression changes underlying TOD.
Materials and Methods We investigated the association between epigenome-wide DNA methylation and five measures of TOD (estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), urinary albumin-creatinine ratio (UACR), left ventricular mass index (LVMI), relative wall thickness (RWT), and white matter hyperintensity (WMH)) in 961 African Americans from hypertensive sibships.
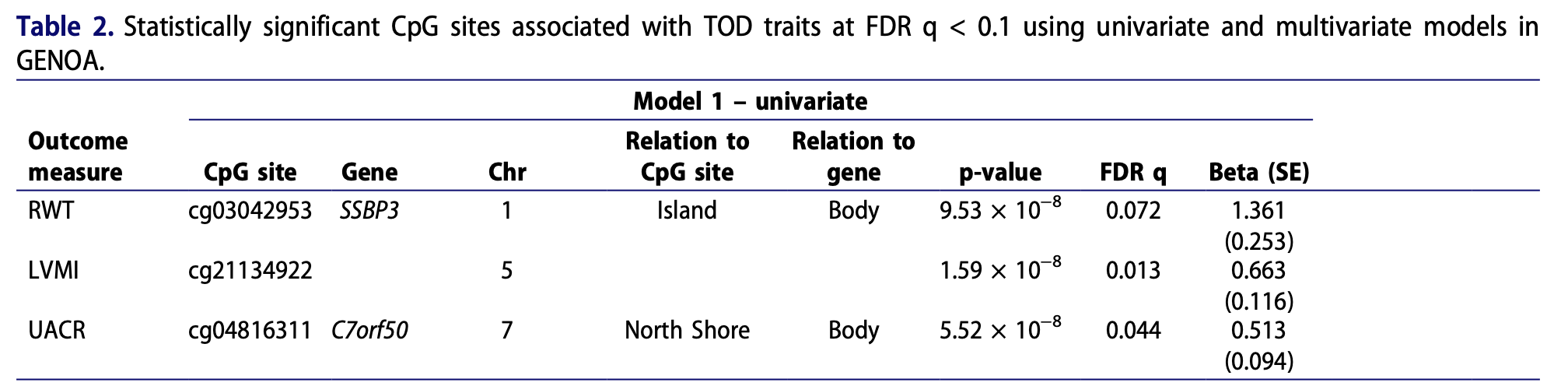
Results A multivariate (multi-trait) model of eGFR, UACR, LVMI, and RWT identified seven CpGs associated with at least one of the traits (cg21134922, cg04816311 near C7orf50, cg09155024, cg10254690 near OAT, cg07660512, cg12661888 near IFT43, and cg02264946 near CATSPERD) at FDR q < 0.1. Adjusting for blood pressure, body mass index, and type 2 diabetes attenuated the association for four CpGs. DNA methylation was associated with cis-gene expression for some CpGs, but no significant mediation by gene expression was detected. Mendelian randomization analyses suggested causality between three CpGs and eGFR (cg04816311, cg10254690, and cg07660512). We also assessed whether the identified CpGs were associated with TOD in 614 African Americans in the Hypertension Genetic Epidemiology Network (HyperGEN) study. Out of three CpGs available for replication, cg04816311 was significantly associated with eGFR (p = 0.0003), LVMI (p = 0.0003), and RWT (p = 0.002).
Conclusion This study found evidence of an association between DNA methylation and TOD in African Americans and highlights the utility of using a multivariate-based model that leverages information across related traits in epigenome-wide association studies.